California State University Sacramento
December 2025 (Sacramento, CA).
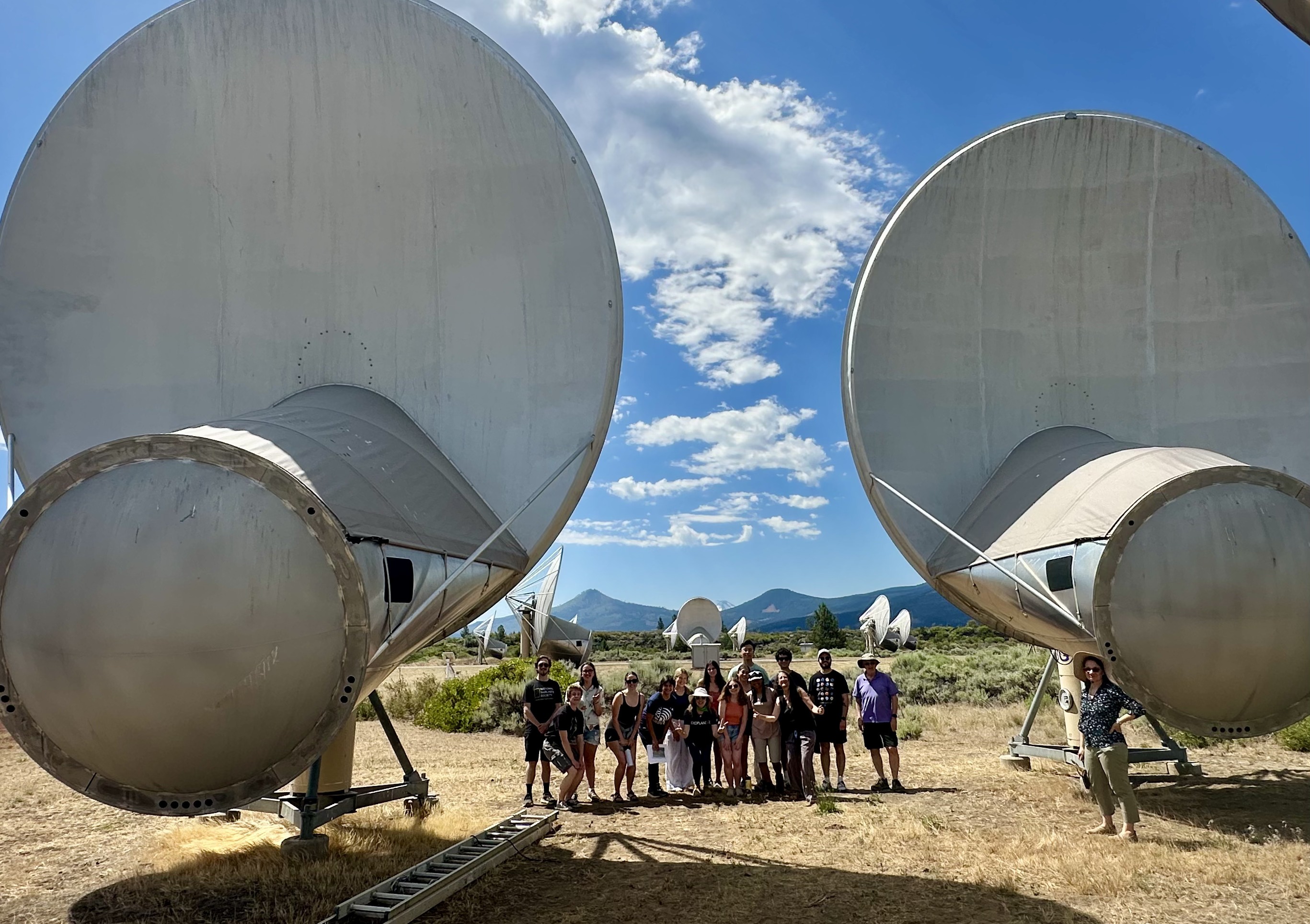
ARISE co-taught ASTR131: Solar System and Space Exploration with Dr. Alexander Pettitt for ~30 students, beginning with a brief introduction to SETI and radio astronomy. The class then ran live demonstrations using the Allen Telescope Array to detect radio signals from the Tianwen-1 spacecraft orbiting Mars (Mars Orbiters and the Search for Technosignatures). We wrapped with a rooftop downlink session using a small radio dish to receive GOES satellite transmissions and connect the resulting data products to “Decoding Earth” as a biosignature-style case study (Decoding Earth: Signals from Geostationary Orbit).